How To Build a Block Garage Step by Step
Building a block garage offers a durable and secure storage solution. This guide provides a comprehensive, step-by-step approach to constructing a standard single-car block garage. It is essential to consult local building codes and obtain necessary permits before commencing any construction project.
Planning and Preparation: Careful planning is crucial for a successful project. Begin by accurately measuring the intended garage site and creating a scaled drawing. This drawing should include the garage dimensions, door placement, window locations (if any), and the position of any electrical outlets or plumbing fixtures. Factor in the thickness of the block walls when calculating overall dimensions.
Foundation: A solid, level foundation is paramount for structural integrity. Mark out the foundation perimeter using stakes and string, ensuring square corners by measuring diagonals. Excavate the foundation trench to the required depth, as specified by local building codes and soil conditions. A layer of compacted gravel forms the base, followed by concrete footings poured into forms. Once cured, concrete block walls, appropriately reinforced with steel rebar, are constructed to form the foundation stem wall.
Slab Preparation: After the foundation cures, the area within the foundation walls is prepared for the concrete slab. Compact a layer of gravel to provide a stable base and ensure proper drainage. A vapor barrier is laid over the gravel to prevent moisture from seeping into the slab. Reinforcing mesh is placed over the vapor barrier before pouring the concrete.
Pouring the Slab: The concrete slab is poured and leveled using a screed board. It's essential to ensure the slab is level and sloped slightly towards the garage door for drainage. The concrete is then finished using a power trowel or hand float, depending on the desired finish. Allow adequate curing time before proceeding to the next step.
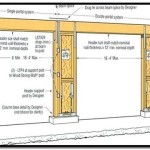
Wall Construction: Laying concrete blocks begins at the corners. The first course of blocks is laid on a bed of mortar, ensuring they are level and aligned. Subsequent courses are staggered to create a strong bond. Vertical reinforcement, typically rebar, is placed at specified intervals within the block cores, which are then filled with concrete. Lintels, made of steel or precast concrete, are installed above door and window openings to support the weight of the blocks above.
Door and Window Installation: Once the walls reach the desired height, install the garage door frame according to the manufacturer's instructions. Secure the frame to the surrounding blockwork and ensure it is plumb and level. If including windows, install them according to their respective manufacturer's instructions, ensuring proper sealing and insulation.
Roof Framing: The type of roof chosen will determine the framing method. Common options include a gable roof, a shed roof, or a flat roof. Construct the roof framing using treated lumber and secure it to the top course of blockwork using anchor bolts. Ensure adequate bracing to provide structural stability.
Roofing: Install the chosen roofing material over the framing. Options include asphalt shingles, metal roofing, or flat roofing materials like EPDM rubber. Ensure proper overlapping and sealing to prevent leaks. Install flashing around any penetrations, such as vents or chimneys, to prevent water intrusion.
Finishing Touches: Once the roof is complete, install gutters and downspouts to direct rainwater away from the garage. Install the garage door according to the manufacturer's instructions. Apply any desired exterior finishes, such as paint or stucco, to the block walls.
Electrical and Plumbing: If including electrical outlets or lighting, engage a qualified electrician to install the wiring and fixtures according to local codes. Similarly, if plumbing is required, engage a licensed plumber for proper installation.
Interior Finishing (Optional): The interior of the garage can be finished according to individual needs. Options include drywall, insulation, and flooring. Shelving and storage cabinets can be installed to maximize storage space.
Landscaping: Grade the area around the garage to ensure proper drainage away from the foundation. Landscaping, such as planting grass or shrubs, can improve the appearance of the finished structure.
This guide provides a general overview of the process. It is crucial to consult local building codes and obtain the necessary permits before starting any construction project. Engaging qualified professionals for specific tasks, such as electrical work and plumbing, is highly recommended.

Block Garage Foundation

How To Brick Up A Garage Step By

How To Build A Concrete Block Shed

How To Build A Garage Framing Diy Family Handyman

Double Garage The Setting Out Floor Prep And Concrete Part 2

Bring Privacy To Your Backyard With A Diy Concrete Block Wall Our Step By Instructions Walls Retaining Blocks

How To Build A Concrete Block Foundation

3 Easy Ways To Extend Your Garage Plus Cost Estimates
Custom Garage Builder In Chicago Il Construction

Multi Car Garage Building Process Design Planning
Related Posts