How Do I Know What Size Torsion Spring I Need For My Garage Door?
Selecting the correct torsion spring size is crucial for the safe and efficient operation of a garage door. Incorrectly sized springs can lead to premature failure, door imbalance, and potential safety hazards. This article provides a comprehensive guide on determining the appropriate torsion spring size for a garage door.
Garage door torsion springs work by storing mechanical energy when the door is closed. As the door is opened, the spring releases this energy, assisting in lifting the weight of the door. The spring's size, measured by its wire diameter, inner diameter, and length, dictates the amount of torque it can generate. Matching the spring's properties to the door's weight is paramount for smooth and reliable operation.
Before attempting any measurements or adjustments to the garage door springs, it is imperative to disconnect the garage door opener and secure the door in the open position. Torsion springs are under significant tension and can cause serious injury if mishandled. It is highly recommended that this process be performed by a qualified garage door technician.
Determining Existing Spring Specifications
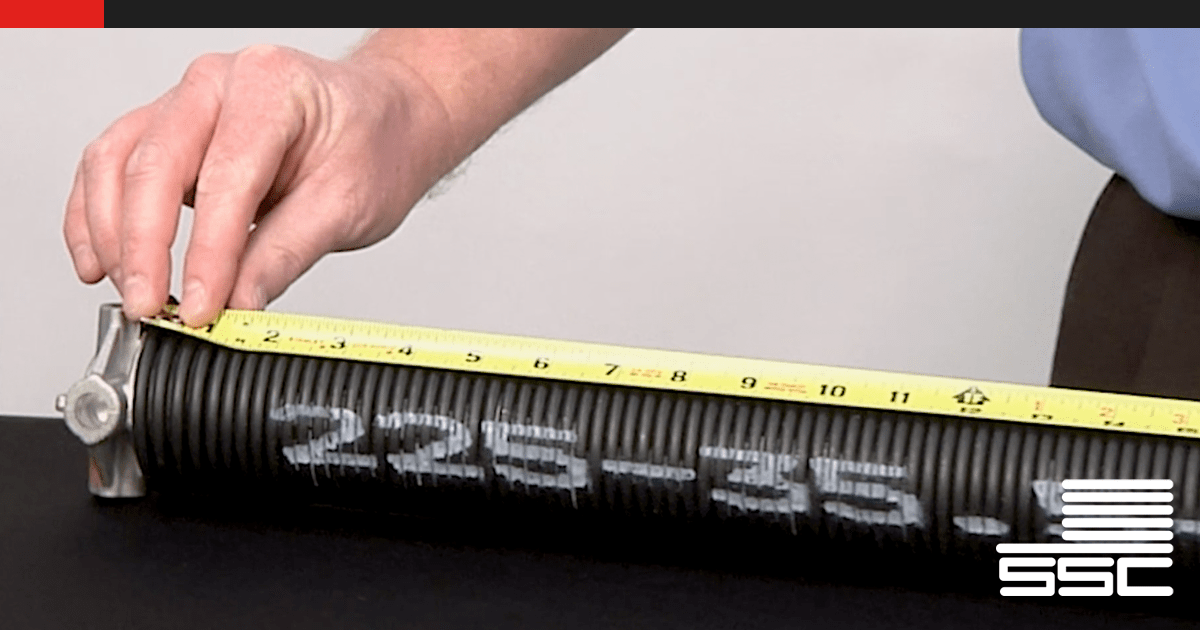
The most reliable method for identifying the correct torsion spring size is to examine the existing springs (if available). This involves carefully measuring the spring's wire diameter, inner diameter, and length. These measurements provide the necessary information to order replacement springs with identical specifications.
Begin by visually inspecting the spring for any remaining paint markings. Many manufacturers color-code their springs to indicate their wire gauge. While this can provide a quick reference, it should not be solely relied upon as paint can fade or be inaccurate. Cross-referencing the color with known color codes is recommended, but measurement should always confirm the result.
To measure the wire diameter, use a pair of calipers. Measure several coils to obtain an accurate average. The wire diameter is typically expressed in thousandths of an inch (e.g., 0.225 inches). This measurement is arguably the most critical, as a slight variation in wire diameter can significantly impact the spring's lifting capacity.
The inner diameter (ID) of the spring is the distance across the inside of the spring coil. Accurately measure the inner diameter using a ruler or tape measure. Most springs have an inner diameter of either 1.75 inches or 2 inches. This measurement is a standard dimension and will primarily affect the selection of the correct winding bars.
Measure the length of the spring while it is relaxed (unwound). This can be difficult if the spring is broken or damaged. In such cases, carefully measure the length of the unbroken portion and extrapolate the total length. The spring length is typically rounded to the nearest inch. Single-spring systems often have a longer spring, while dual-spring systems utilize two shorter springs.
After obtaining the wire diameter, inner diameter, and length, note the spring's wind direction. A right-wound spring will have its coils winding upwards to the right, while a left-wound spring will wind upwards to the left. This is crucial for correct installation and spring orientation. Usually, when standing inside the garage facing the door, the right-wound spring will be on the left side of the door, and the left-wound spring will be on the right side.
Calculating Spring Requirements Based on Door Weight and Height
If the existing spring specifications are unavailable, the required spring size can be calculated based on the garage door's weight and height. This method involves several steps and requires careful attention to detail.
First, accurately determine the weight of the garage door. This can be accomplished by weighing the door directly using scales or by referring to the manufacturer's specifications. If the manufacturer's data is unavailable, estimating the weight based on the door's material and dimensions is necessary. Steel doors are generally heavier than aluminum or wood doors of the same size.
Measure the height of the garage door in inches. This measurement is required to calculate the required torque. Standard garage doors are typically 7 or 8 feet tall. However, custom-sized doors may require adjustments to the calculations.
Once the door weight and height are known, the required torque can be calculated. The formula for calculating torque is: Torque = (Door Weight / 2) * (Door Height in Feet). This calculation provides the total torque required to lift the door.
Next, consult a torsion spring chart or online calculator to determine the appropriate spring specifications based on the calculated torque. These charts provide a range of spring sizes that can handle the required torque. Select a spring with a torque rating that is slightly higher than the calculated torque to ensure adequate lifting capacity and prevent premature spring fatigue. The spring chart or calculator will use the wire diameter, inner diameter, and spring length to calculate the torque rating.
It's important to understand that the spring calculations are an estimation. Factors such as door construction, lubrication, and hardware friction can affect the required torque. It is recommended to consult with a garage door professional for accurate calculations and spring selection, especially for heavier or custom-sized doors.
Considering Single vs. Dual Spring Systems
Garage doors can utilize either a single torsion spring or a dual torsion spring system. The choice between these systems depends on the door's weight, size, and the manufacturer's design.
Single-spring systems typically utilize a longer, heavier spring to provide the necessary lifting force. These systems are often found on lighter, single-car garage doors. If a single spring breaks, the entire door becomes inoperable and can pose a safety hazard. Replacing a single spring requires careful tensioning and can be more challenging than replacing dual springs.
Dual-spring systems utilize two shorter springs, each contributing to the overall lifting force. These systems are commonly found on heavier, double-car garage doors. If one spring breaks in a dual-spring system, the door may still be partially operable, but immediate repair is still recommended. Dual-spring systems offer a degree of redundancy and can be easier to balance and tension.
When replacing springs in a dual-spring system, it is crucial to replace both springs simultaneously, even if only one spring is broken. This ensures that both springs have the same tension and wear characteristics, preventing imbalance and premature failure of the remaining spring. Failure to replace both springs can lead to uneven door operation and increased stress on the system.
Conversion from a single-spring system to a dual-spring system is possible but requires significant modifications to the garage door hardware and support structure. It is advisable to consult with a garage door professional before attempting such a conversion to ensure proper installation and safe operation.
Selecting the appropriate torsion spring size is a critical safety consideration. Incorrectly sized springs can result in door imbalance, premature spring failure, and potential injury. It is recommended to consult with a qualified garage door technician for accurate spring selection and professional installation. The cost of professional service is often justified by the safety and long-term reliability of the garage door system.
Before ordering springs, always double-check all measurements and specifications. Pay close attention to wire diameter, inner diameter, length, and wind direction. Verify that the selected springs are compatible with the garage door hardware and track system. Ordering incorrect springs can lead to delays and additional costs.
Properly tensioning the torsion springs is essential for smooth and balanced door operation. Incorrect tension can cause the door to be difficult to open or close, or to move unevenly. Tensioning torsion springs requires specialized tools and knowledge. It is highly recommended that this procedure be performed by a qualified garage door technician.
Regular maintenance, including lubrication of the springs and hardware, can extend the lifespan of the torsion springs and ensure proper door operation. Inspect the springs regularly for signs of wear or damage. Replace worn or damaged springs promptly to prevent potential safety hazards.

How To Choose The Right Garage Door Springs For Your Home Ogd

Garage Door Spring Size Chart Heritage

How To Choose The Right Garage Door Springs For Your Home Ogd

5 Things To Determine The Correct Garage Door Spring Size Ssc
How To Measure And Order Torsion Springs Ssc

How To Measure Garage Door Springs

How To Measure Garage Door Torsion Springs

5 Things To Determine The Correct Garage Door Spring Size Ssc

5 Things To Determine The Correct Garage Door Spring Size Ssc

How To Measure Garage Door Torsion Springs Idc Spring
Related Posts








